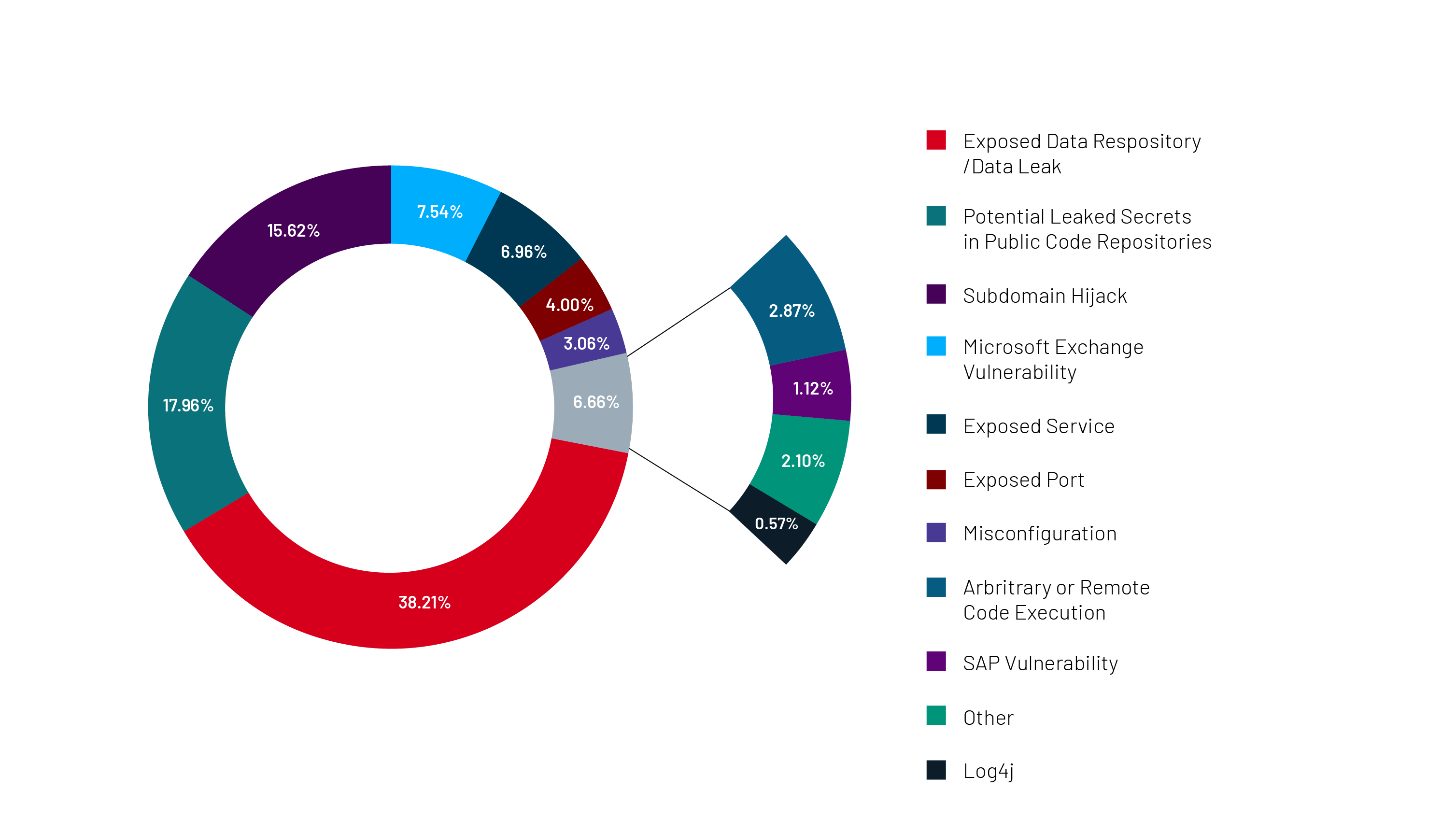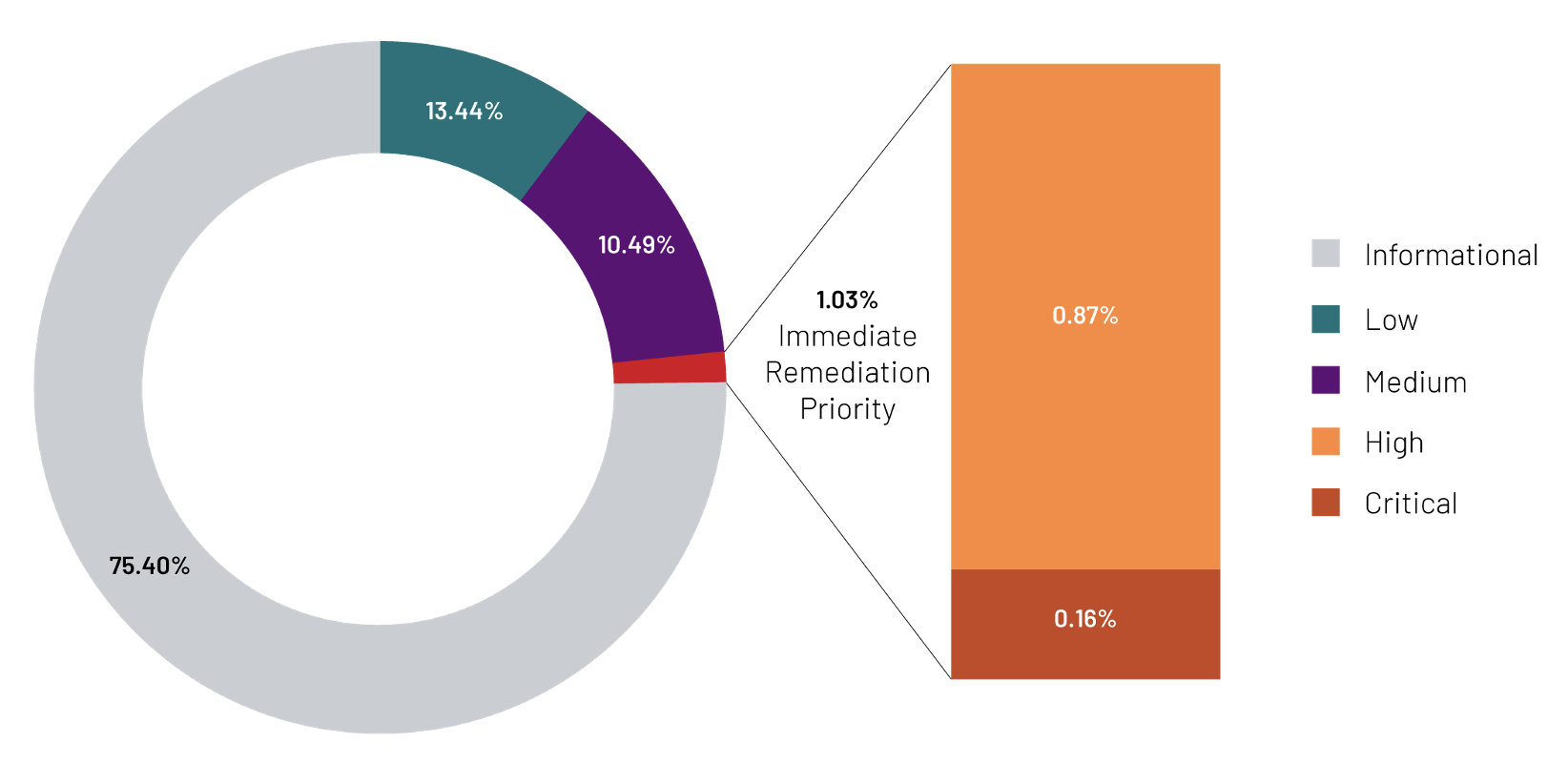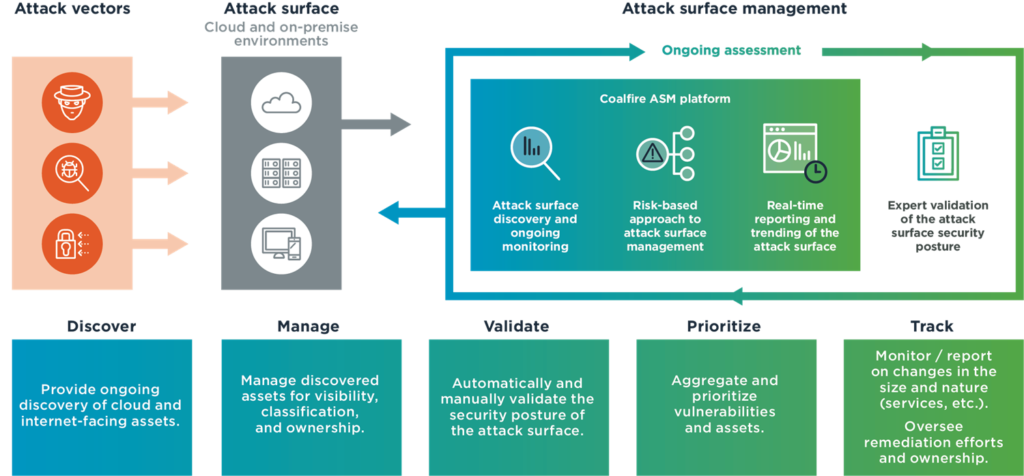
Introduction
In today’s ever-evolving threat landscape, organizations must continuously evaluate and enhance their security measures to protect against potential cyber attacks. Penetration testing, a vital component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, allows businesses to proactively identify vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of their security defenses. In this blog post, we will delve into the latest practices in penetration testing, including API testing, application testing, external networks, internet-facing infrastructure, and more. By adopting these practices, organizations can bolster their security defenses and mitigate potential risks.
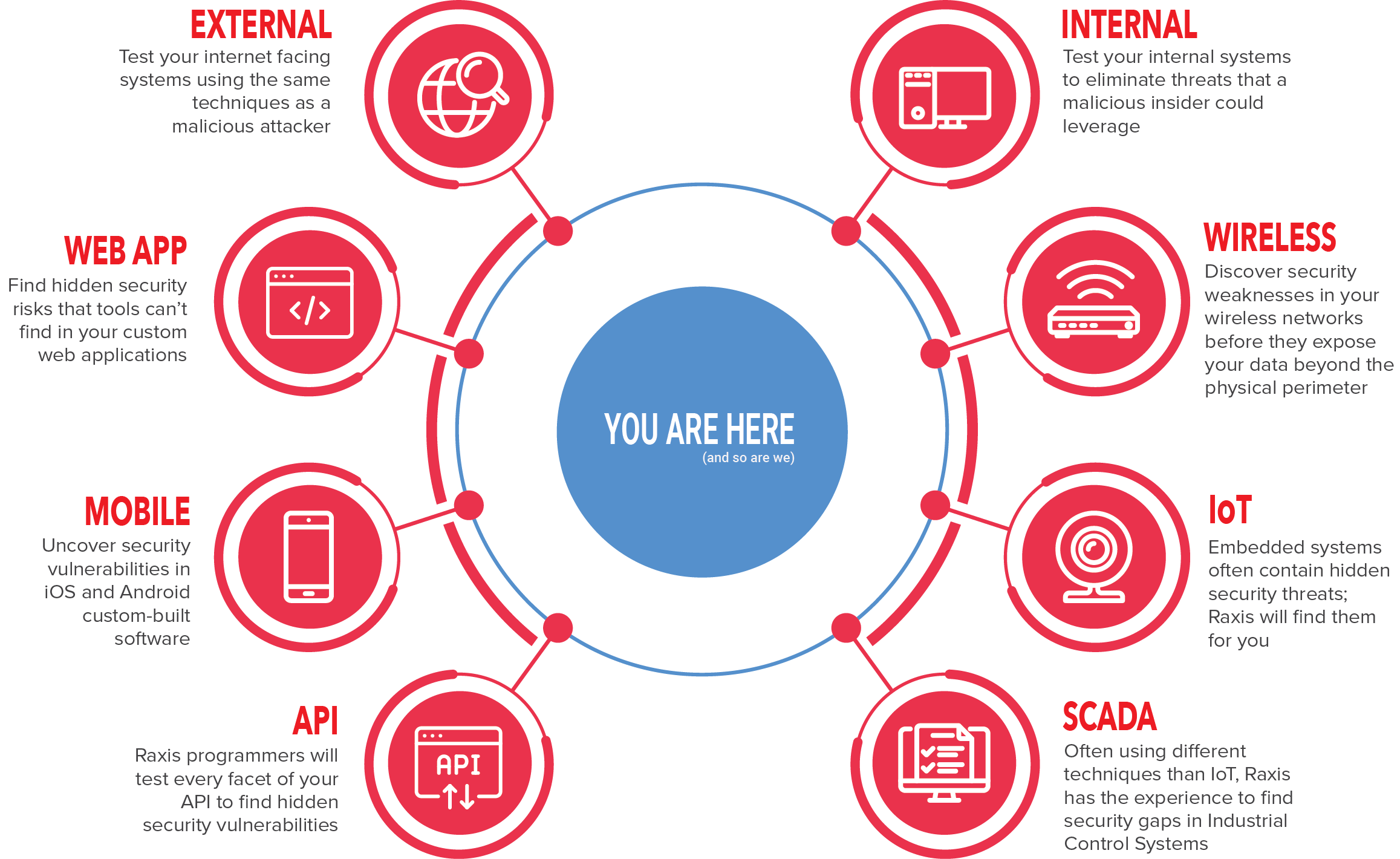
- API Testing:
With the increasing prevalence of application programming interfaces (APIs), it is crucial to include API testing in penetration testing efforts. APIs serve as a gateway for data exchange between different systems and are often targeted by attackers. API testing involves assessing the security of API endpoints, authentication mechanisms, data validation, and access controls. By scrutinizing APIs for vulnerabilities, organizations can prevent unauthorized access, data leaks, and potential API-based attacks.
- Application Testing:
Applications, both web-based and mobile, represent significant attack vectors. Penetration testing of applications involves assessing the security of the underlying code, the robustness of authentication and authorization mechanisms, input validation, session management, and data storage practices. By thoroughly testing applications, organizations can identify vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, and insecure direct object references, and remediate them before they are exploited by malicious actors.
- External Network Testing:
External network testing focuses on evaluating the security of an organization’s network perimeter. It involves identifying vulnerabilities in firewalls, routers, VPNs, and other network devices that connect to the internet. By conducting external network penetration tests, organizations can identify potential entry points for attackers, assess the effectiveness of network security controls, and fortify their network defenses.
- Internet-Facing Infrastructure Testing:
Organizations often have internet-facing infrastructure, such as web servers, DNS servers, and mail servers, which are susceptible to attacks. Penetration testing of internet-facing infrastructure aims to uncover vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers to compromise these critical assets. By assessing the security of these systems, organizations can ensure that they are properly hardened, patched, and protected against potential threats.
- Social Engineering Testing:
Humans remain one of the weakest links in cybersecurity. Social engineering testing involves simulating various techniques, such as phishing emails, pretexting, and impersonation, to assess an organization’s susceptibility to manipulation and deception. By raising awareness and educating employees about social engineering attacks, organizations can minimize the risk of falling victim to such tactics.
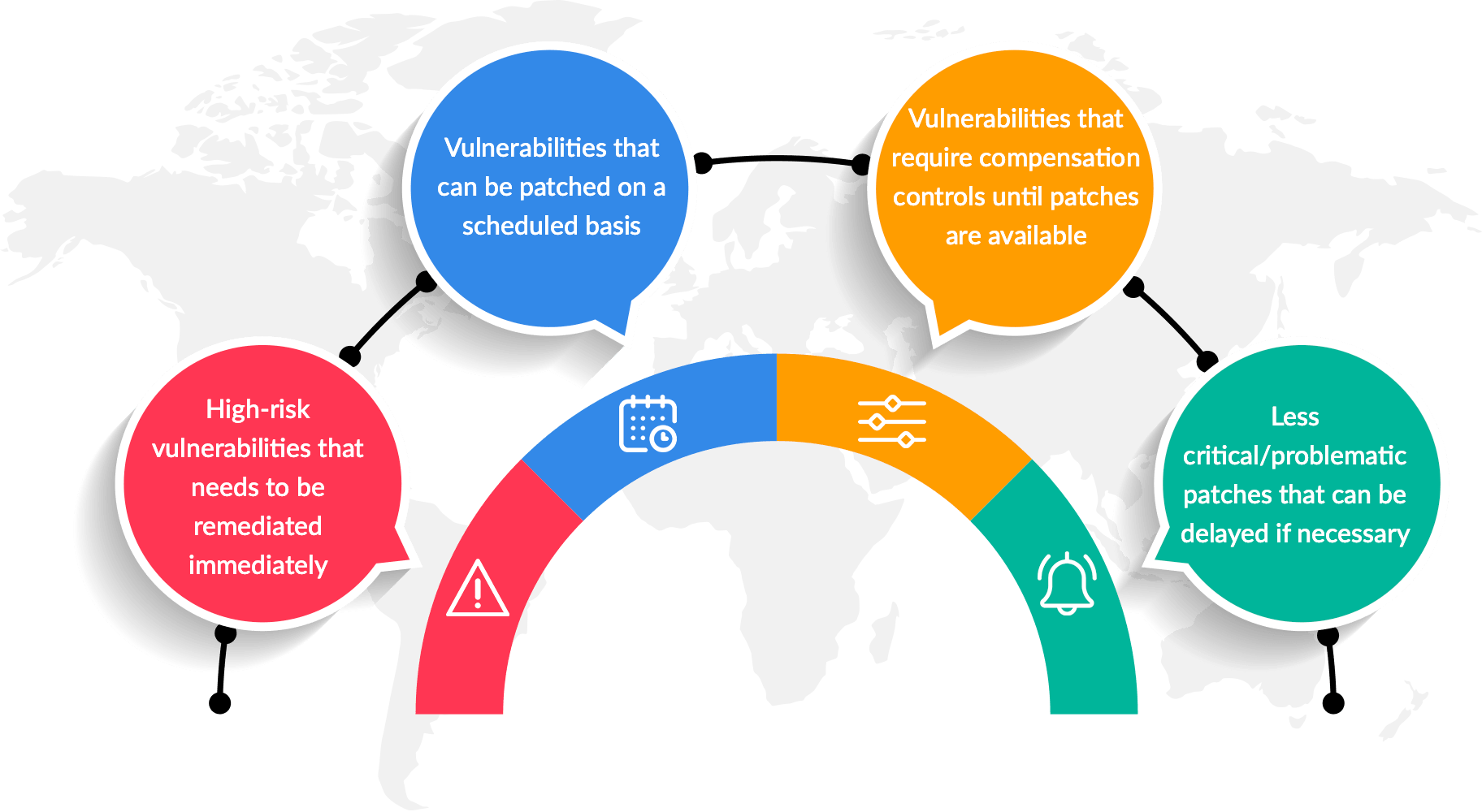
Benefits of Following Latest Penetration Testing Practices:
- Enhanced Security: By adopting the latest practices in penetration testing, organizations can identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they are exploited by attackers, thereby enhancing their overall security posture.
- Compliance: Following best practices in penetration testing helps organizations meet industry regulations and compliance requirements by conducting regular security assessments.
- Risk Mitigation: Thorough testing of APIs, applications, external networks, and internet-facing infrastructure reduces the attack surface and minimizes the risk of successful cyber attacks.
- Cost Savings: Identifying and fixing vulnerabilities during the testing phase is more cost-effective than dealing with the aftermath of a security breach, which can result in financial losses, reputation damage, and legal consequences.
- Continuous Improvement: Staying up to date with the latest practices in penetration testing ensures that organizations keep pace with emerging threats, evolving technologies, and industry trends, enabling them to adapt and improve their security defenses.
Conclusion:
By following the latest practices in penetration testing, organizations can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities across various attack vectors. Conducting thorough testing of APIs, applications, external networks, internet-facing infrastructure, and employing social engineering assessments