Introduction
In the digital age, where organizations rely heavily on information systems and technology, the need for robust and secure IT environments has become paramount. Information Systems (IS) Audit serves as a critical component in ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of digital assets. In this blog post, we will explore the world of IS Audit, its significance, processes, and the benefits it offers to businesses.
Understanding IS Audit:
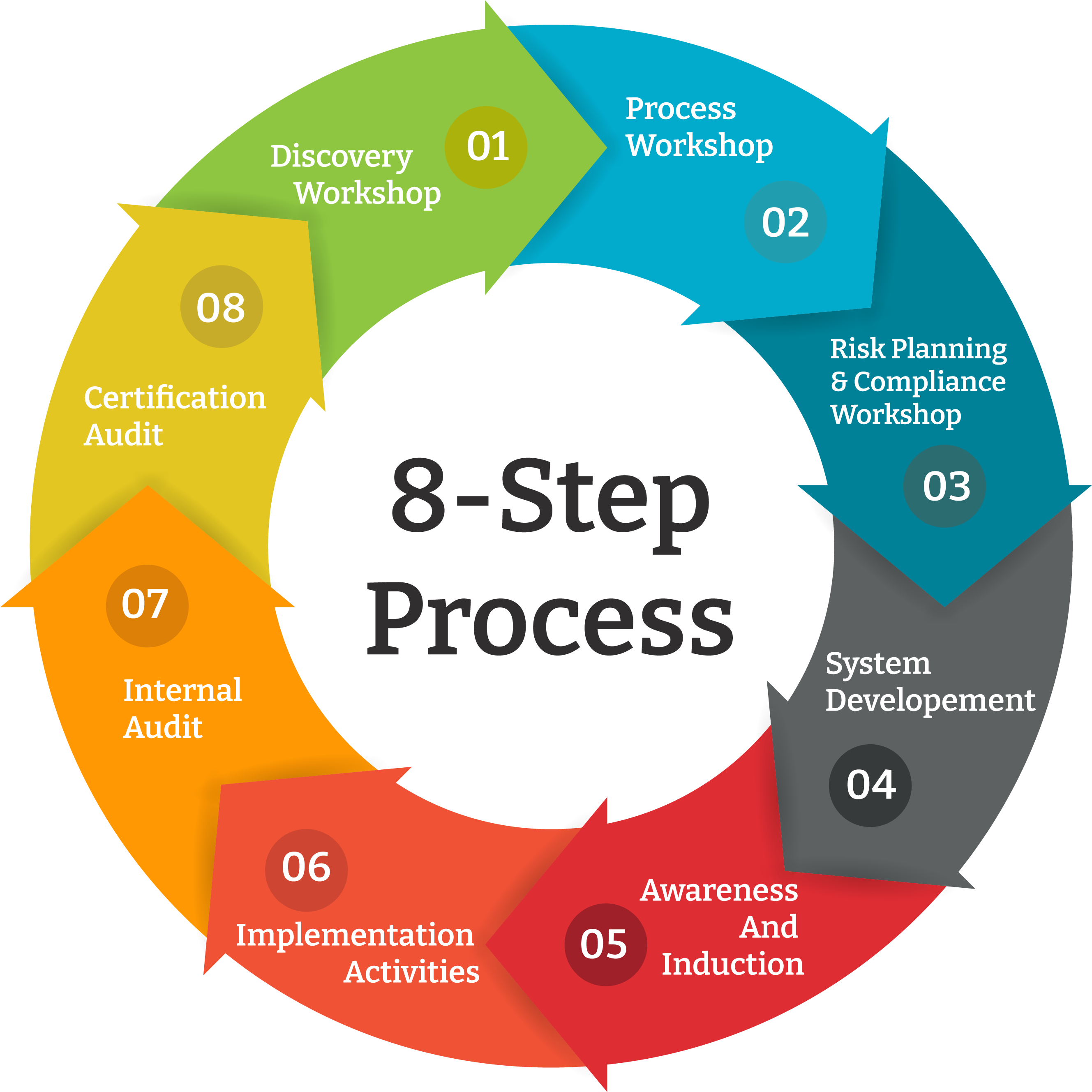
IS Audit, also known as IT Audit or Information Technology Audit, is a systematic evaluation of an organization’s IT infrastructure, policies, procedures, and controls. It aims to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of information systems, identify vulnerabilities, and provide recommendations to enhance the security and overall governance of IT resources.
The primary objectives of IS Audit include:
- Evaluating Compliance: Ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal policies to minimize legal and operational risks.
- Assessing Security: Identifying vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and potential threats to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems.
- Evaluating Controls: Reviewing the effectiveness of IT controls, such as access controls, change management, data backup, and disaster recovery mechanisms.
- Enhancing Efficiency: Identifying opportunities for process improvement, cost reduction, and optimization of IT resources.
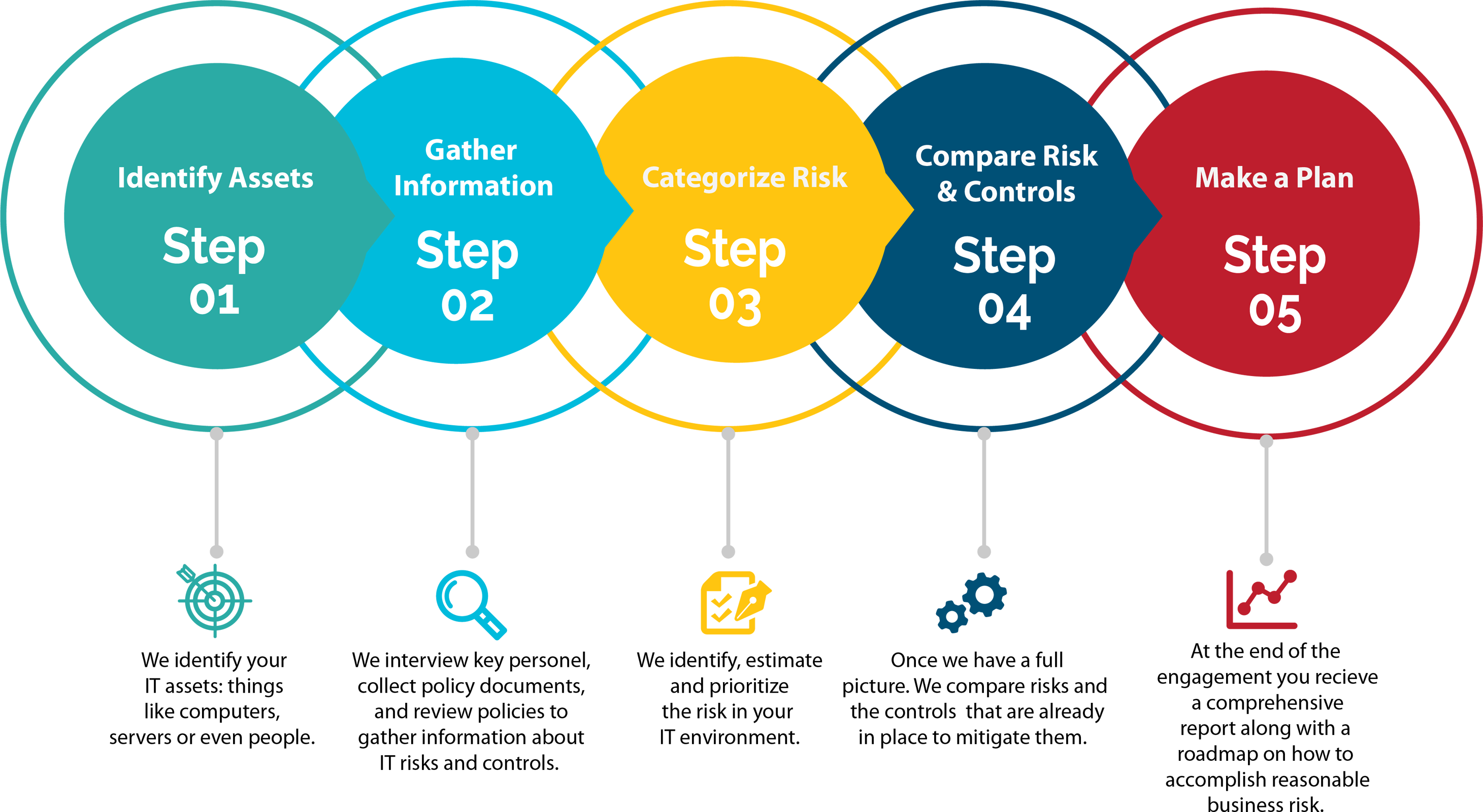
The IS Audit Process:
- Planning: Defining the scope, objectives, and methodologies for the audit, including identifying critical areas, systems, and potential risks.
- Data Collection: Gathering information about IT systems, policies, procedures, and controls through interviews, documentation review, and data analysis.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of potential risks to prioritize audit activities and allocate resources effectively.
- Testing and Evaluation: Assessing the adequacy and effectiveness of controls through various techniques, including sampling, system analysis, and vulnerability assessments.
- Reporting: Documenting audit findings, including identified risks, control weaknesses, and recommendations for improvement. Reports typically highlight strengths, weaknesses, and areas requiring management attention.
Benefits of IS Audit:
- Risk Mitigation: IS Audit helps identify vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and potential risks, allowing organizations to implement controls and measures to mitigate those risks effectively.
- Compliance: By assessing adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards, IS Audit helps organizations ensure compliance and avoid legal and operational consequences.
- Enhanced Security: Through the evaluation of security controls, IS Audit helps identify gaps and provides recommendations to strengthen the security posture, protecting sensitive data and information assets.
- Process Improvement: IS Audit identifies inefficiencies, redundancies, and areas for improvement in IT processes, leading to enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and optimized resource utilization.
- Stakeholder Confidence: A comprehensive IS Audit demonstrates an organization’s commitment to robust IT governance, security, and risk management. This builds trust and confidence among stakeholders, including customers, partners, and investors.
Conclusion:
In an era where digital assets are integral to business operations, IS Audit plays a vital role in ensuring the integrity, availability, and security of information systems. By evaluating controls, identifying risks, and recommending improvements, IS Audit helps organizations establish a robust IT governance framework, comply with regulations, and safeguard critical assets. Embracing IS Audit as an ongoing practice allows businesses to adapt to evolving threats, build resilience, and maintain trust in the digital realm.
